Stairways And Ladders
The material in this article is extracted from Chapter 2 of the 2nd edition of book Plant Design and Operations. The guidance provided here should always be evaluated for specific conditions.
When developing the layout for a facility it is very important to ensure that personnel can move around quickly and safely using stairways, ladders, platforms and ramps. They should also be able to use the stairways and ladders to move maintenance equipment and tools, as needed and also to evacuate the facility during an emergency.
In terms of convenience and safety ramps are generally preferred over stairways, which in turn are preferred over ladders. Stairs should generally be used over ladders in the following situations:
When routine movement between two levels is required.
For routine tasks such as gauging, inspection and maintenance.
Employees could be hand-carrying heavy or bulky tools and/or equipment.
When there is a potential for exposure to hazardous materials at the elevated location and immediate escape is required.
Ramps are used in areas where there is high traffic and/or frequent use of wheeled carts that are used to move equipment.
The design of stairways, ladders and platforms is covered by many regulations and standards, some of which are listed in Table 2.1.
Stairways
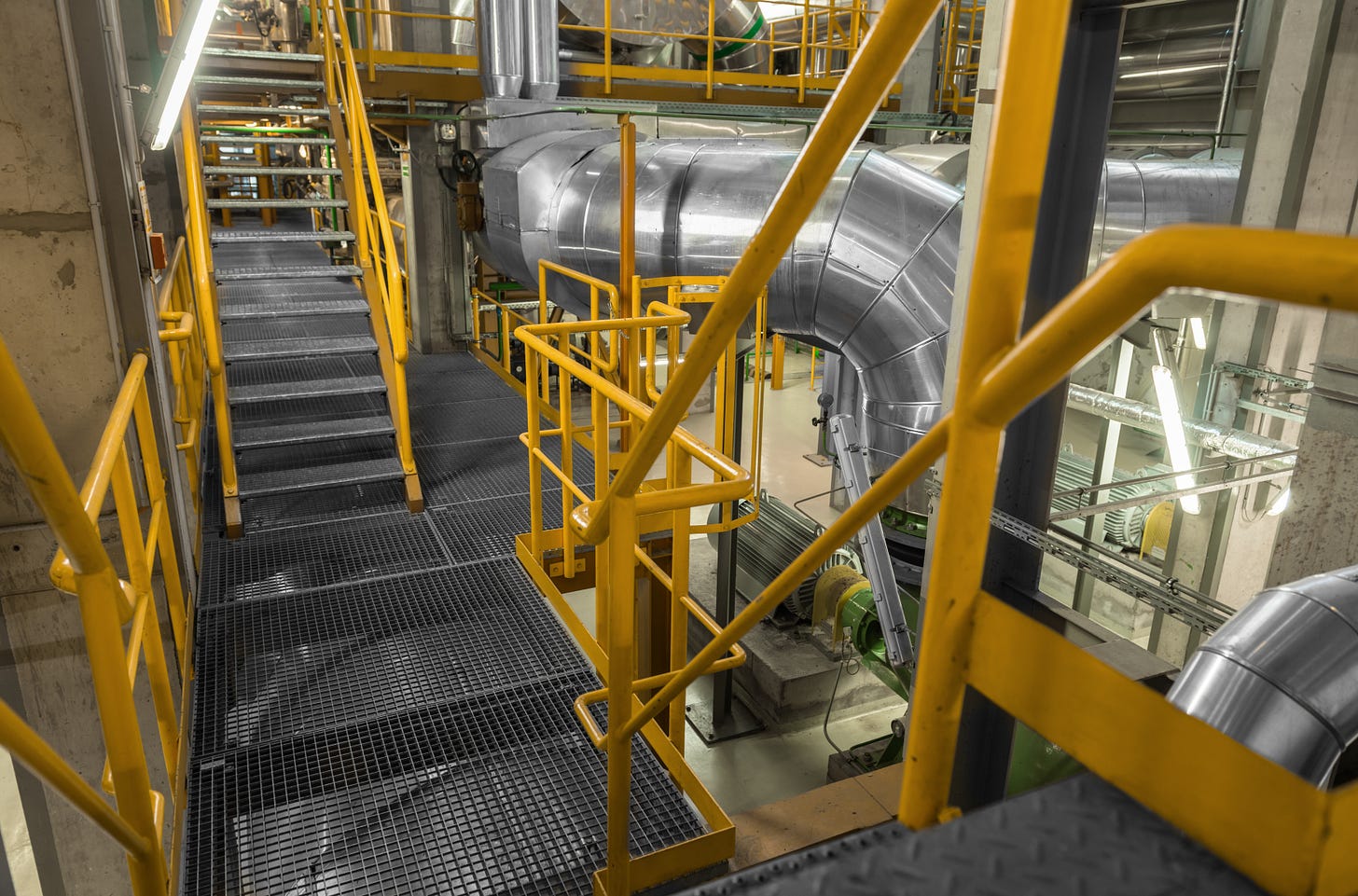
Stairways are the normal method of moving from one level to another, particularly for routine operations and for emergency evacuation. Spiral stairs should not generally be used although winding stairs can be installed on tanks, as discussed in the next chapter.
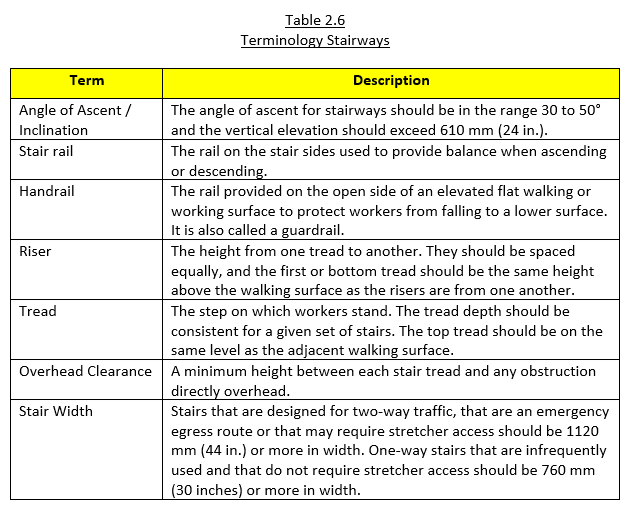
The picture is of a typical industrial stair as found in the process and energy industries. The terminology used to describe the different parts of the stair are provided in Table 2.6.
The following guidance can be used when designing stairway. It is important to evaluate each case on its own merits ― perhaps with a hazards analysis.
Maximum angle with a horizontal line: 45 degrees.
Minimum effective tread depth: 280 mm (11 in.)
Minimum effective width of stair: 750 mm (2 ft. 6 in.).
Stair landings: not less than 750 mm (2 ft. 6 in.) in the direction of the stairway.
Guard railings and toe plates should be according to ASSE A1264.1. Guard railings should be constructed of structural steel shapes or pipe. Any pipe railing should be seal welded to prevent internal corrosion.
Landings
If a stair has a vertical rise of 6 m. or more intermediate landings should be provided every 3.5 meters. (Occasional use stairways may not require intermediate landings.) The landings should be as wide as the stairs and should have handrails.
Where doors or gates open directly on a stairway, a platform should be provided; the swing of the door should not reduce the effective width to less than 20 inches (600 mm).
Load Capacity
Stairways should be built to carry five times the normal anticipated live load, but not less than a 450 kg/1000 lbs. moving concentrated load. The design load for walkways and platforms should be the maximum probable loads produced by the intended use. The design load should be increased as necessary for any machinery or equipment which may add to the live load.
Stair Rails
Railings are required for floors and stairways that have open sides, and for platforms that have a significant elevation over the deck/grade around them. The following guidance to do with the design of stairs is provided.
A single-tier stair rail is used to maintain balance while going up or down stairs, and should be installed on the enclosed side of stairs.
A two-tier rail, used to maintain balance and prevent falls from stairs, should be installed on all open sides of stairs.
Stairs with three or more steps should be equipped with stair rails.
Stairs wider than 2240 mm (88 inches) should be equipped with a single-tier stair rail in the center.
Stair rails should be highly visible, often of a different color from the stairs themselves.
Toeboards are required if a person could slip under a railing.
Stair Treads
Each tread should be painted to make its leading edge visually distinctive from the color of the rest of the tread or the walking surfaces to which it is connected. When the stair tread and/or deck grating is yellow the leading edge should be painted a bright red. When the stair treads and/or deck grating is galvanized steel or painted a gray color, the leading edge should be painted a bright yellow.
All treads should be slip resistant; steel stairs should have treads made of serrated grating. If floor plate is used then weep holes for drainage should be provided.
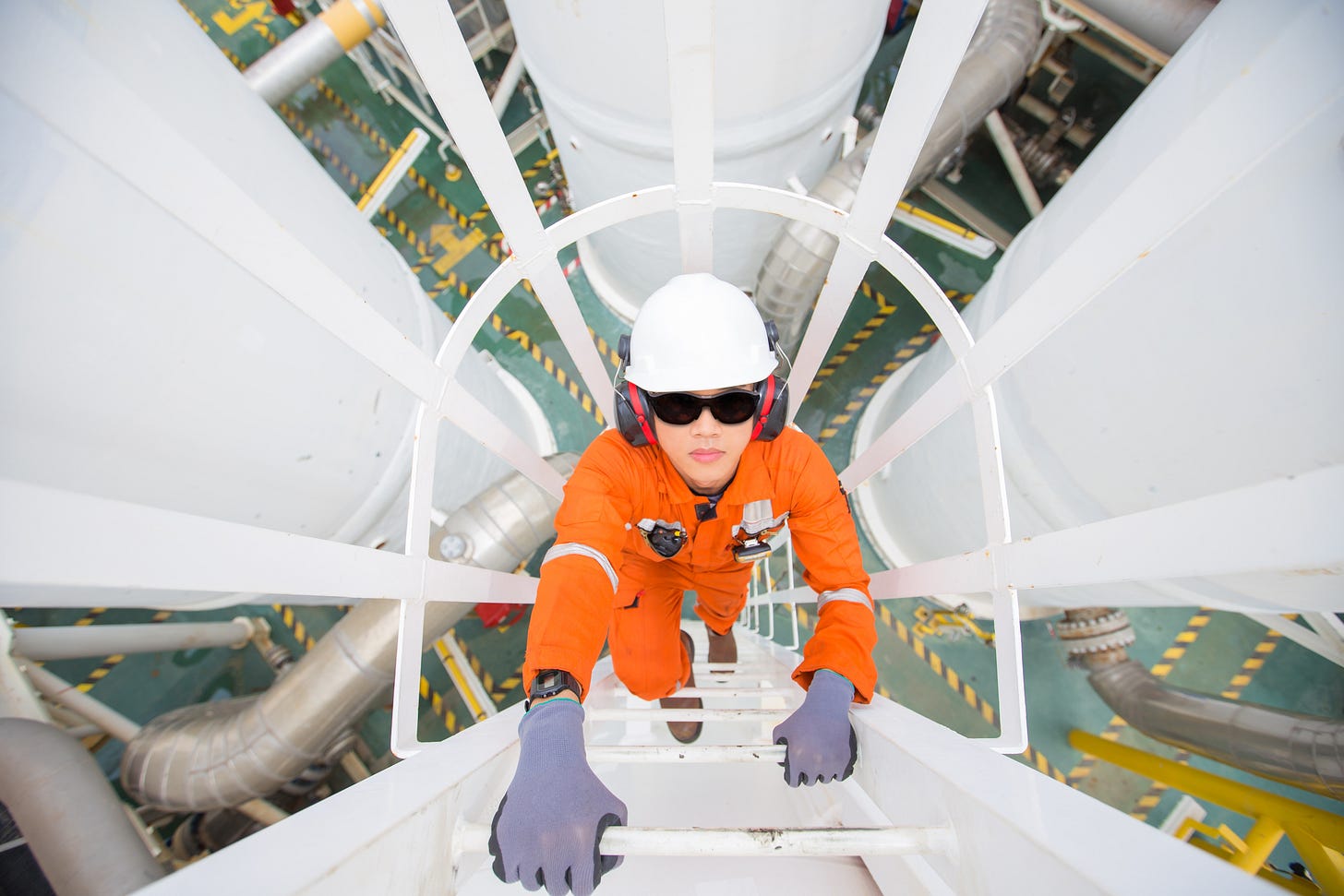
Ladders
Ladders are typically used in the following applications:
Access to elevated tanks, towers and overhead traveling cranes;
Secondary access and escape;
Maintenance access to platforms or other access which are used infrequently or where stairways are impractical.
They should never be used as the primary mode of escape, nor should they be used as work platforms. If ladders provide access to a work site on the side of tank, vessel or other structure then a work platform should be provided so that he or she can safely use both hands and is protected from falling if they lose balance.
The design and use of ladders offshore poses special concerns, including the following. Ladders should not be installed near deck edges, where possible. A fall from the deck could be much greater than the ladder height.
Dimensions
The design and installation of fixed ladders should consider the following guidelines (all measurements are approximate, and will vary according to local standards and regulations):
Ladders should be vertical whenever possible. Where clearance problems require the ladder to be sloped, the slope should not exceed 15° forward and should not slope backward under any circumstances. The angle of inclination for fixed vertical ladders should be between 75° and 90° from the horizontal.
Fixed ladders should be straight throughout their length.
Ladders should be oriented so that a person faces the structure or vessel while climbing.
Side access ladders are preferred to the front access style for the reasons referred to above.
The design load should be determined by the anticipated usage of the ladder, but not less than a single concentrated load of about 120 kg or a moving concentrated load of 227 kg (500 lbs.).
The minimum clear length of rungs or cleats should be 0.4 meter.
Rungs and side rails should be free of splinters, sharp edges, burrs or projections which may be a hazard.
Side rails which might be used as a climbing aid should be of such cross sections as to afford adequate gripping surface without sharp edges, splinters, or burrs.
The perpendicular distance on the climbing side of the ladder from the centerline of the rungs to the nearest permanent fixed object should be 1 meter or more.
The perpendicular distance on the back side of the ladder from the centerline of the rungs to the nearest permanent fixed object should be 200 mm or more, except when unavoidable obstructions are encountered.
The step across distance from the nearest edge of the ladder to the nearest edge of equipment or structure should not be more than 0.4 meters.
Ladder rungs should be equally spaced throughout, including the first rung below the landing.
Ladder extensions should extend at least 3 meters above parapets and landings.
Rung spacing should be around 0.3 meter center to center and should be uniformly spaced throughout the length of the ladder.
A barrier should be placed on the back side of ladders that could be inadvertently climbed on the wrong side.
Ladder rungs should be made of steel, protected from corrosion, and made of non-slip materials.
Maximum heights of unbroken ladders should be 30 ft. (9145 mm) for ladders with cages and 6100 mm (20 ft.) for ladders without cages. Where vertical ladder heights exceed 9145 mm (30 ft.), intermediate landings and separate, multiple ladder runs of equal length should be provided to cover the required vertical distance.
There should be a rest platform every 10 meters.
Where transition from one vertical ladder to another is accomplished using a side-step platform, the horizontal separation between the two ladders should be a maximum of 460 mm (18 inches). A rung on the parallel ladder to the intermediate platform should be at the same height as the platform.
All vertical ladders must be attached to permanent structures, and should not be attached to removable items (e.g., manways or handrails), or interfere with the removal of any item.
Ladders should be located so the maximum distance from ladder centerline to any object, which must be reached by a worker from the ladder, should not exceed 760 mm (30 in.).
Vertical ladders used to access tank openings or pressure vessel manways or any other opening equipped with a hinged cover should be located so the cover swings away from the ladder.
More rigorous standards apply to ladders and related equipment that is in the wave zone of an offshore platform.
Safety Cages and Gates
Fixed ladders should have a cage around them so that, were a worker to fall, he or she would fall down, not out. Ideally the bottom exit from the ladder cage should be oriented at 90° from the ladder itself. There have been occasions where a person fell down a ladder, hit the platform or deck, and then fell over the handrail down to the level below, in at least one case resulting in a fatality on an offshore platform that was under construction.
Two incidents that resulted in fatalities and which involved vertical ladders occurred at about the same time. These incidents led to the adoption of the following company standard.
When a caged ladder is located within 6 ft. of the edge of the deck, which has a maximum fall distance greater than 15 ft., special consideration is required. Either the bars on the cage on the deck edge side should be extended to the handrail, or the handrails should be raised to within 24 in. of the bottom of the safety cage for 48 in. on either side of the ladder centerline. The extended bars on the cage should not restrict access to the ladder or to the walkway.
The ladders should terminate such that the person using them sidesteps on to the platform. This will result in a person being able to see where he is placing his feet. The sidestep configuration has another advantage in that requires no transfer of the hands from the ladder rungs to the stringer when reaching the top.
A self-closing safety gate covering the full width of the opening between the ladder stringers should be installed at the top of each ladder. A safety gate should meet the following standards.
Resist the full weight of a person in both the vertical and horizontal direction.
Where ladders provide access to small platforms that do not provide sufficient space for the self-closing gate to swing horizontally, manually operated gates that open and close via a vertical swing should be used.
The gate should open away from the person climbing up the ladder.
Chains should not be used.
Rungs and Stringers
Ladder rungs should be used to hold on to when climbing. The use of stringers should be discouraged because there is an increased chance that their hand will slip. Angular or flat bar increases the chances of someone’s hand slipping, and should not be used.
The following general guidance applies to the design of the rungs on a ladder.
The top rung (as well as the top rung used to access an intermediate platform) on all vertical ladders should be top flush with the top walking surface (or side-step platform).
Vertical spacing between the centerline of the rungs should be between 280 mm (11 inches) and 300 mm (12 inches) depending on what is required to provide equal spacing between rungs for the entire length of the ladder from the bottom landing to the top rung.
Where multiple runs of ladder lengths are required to cover the vertical distance, the same rung spacing should be used for all run lengths where possible.
The top surface of a rung should be covered with a non-slip material; especially where ice or snow is expected.
There should be a stringer on each side of the ladder for the full length of the ladder.
There should be a clear distance behind the rungs of approximately 8 inches (205 mm).
There should be no obstructions above the top rung.